Stay Active and Exercise Regularly:

Our bodies are designed to move, and regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy heart. Engaging in exercise not only helps to strengthen the heart muscle but also improves blood circulation throughout the body, reducing the risk of cardiac arrest.
You don’t have to become a gym rat or spend hours working out each day. Find activities that you enjoy and make them part of your routine. Whether it’s going for brisk walks, dancing, swimming, or playing a sport, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
Remember to listen to your body and start slowly if you’re just getting started with exercise. Gradually increase intensity and duration over time as your fitness level improves. And don’t forget to stay hydrated during workouts by drinking plenty of water.
Incorporating physical activity into your daily life doesn’t have to be complicated, either. Take the stairs instead of using elevators whenever possible, park farther away from entrances to get in some extra steps, or even try doing household chores more vigorously – every bit counts!
Maintain a Heart-Healthy Diet:

Maintaining a heart-healthy diet is crucial for reducing the risk of cardiac arrest. The food we eat has a direct impact on our cardiovascular health, so it’s important to make smart choices when it comes to our meals.
Try incorporating plenty of fruits and vegetables into your diet. These nutrient-rich foods are packed with antioxidants that help protect against heart disease. Opt for colorful options like berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits.
Whole grains should also be a staple in your diet. They provide essential fiber and nutrients that support heart health. Choose whole wheat bread, brown rice, quinoa, and oats over refined grains.
When it comes to fats, opt for healthy sources such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These contain monounsaturated fats which can help lower bad cholesterol levels.
Limiting saturated fats found in red meat and full-fat dairy products is important, as they can raise cholesterol levels. Instead, choose lean proteins like fish (rich in omega-3 fatty acids), skinless poultry, beans, legumes, or tofu.
Lastly, but importantly: Stay away from excessive salt intake! High sodium consumption can lead to high blood pressure, which increases the risk of heart disease.
Manage Stress:

Stress has become an inevitable part of our lives, but managing it effectively is vital. Chronic stress can have a direct impact on our heart health and overall well-being. So, how can we manage stress and protect our hearts?
It’s important to identify the source of your stress. Is it work-related? Relationship issues? Financial worries? Once you pinpoint the root cause, you can take steps to address it.
One effective way to manage stress is through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga. These practices help calm the mind and reduce tension in the body.
Another strategy is to engage in activities that bring you joy and provide an outlet for stress relief. This could be anything from pursuing a hobby or spending time with loved ones to engaging in physical activity like walking or cycling.
Additionally, making time for self-care is essential. Prioritize getting enough sleep, eating nutritious meals, and taking breaks throughout your day to recharge.
Don’t hesitate to seek support when needed. Talking to a trusted friend or family member about your feelings can provide valuable perspective and emotional release.
Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Intake:

One of the most important steps you can take to reduce your risk of cardiac arrest is to avoid smoking and limit your alcohol intake. Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, including heart attacks and sudden cardiac arrest.
Smoking damages blood vessels and decreases oxygen levels in the blood, making it harder for your heart to pump effectively. It also increases the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to a higher risk of blockages.
Similarly, excessive alcohol intake can lead to high blood pressure, an irregular heartbeat, and weakened heart muscles. It can also contribute to obesity and increase triglyceride levels in the bloodstream, both of which are risk factors for cardiovascular problems.
If you’re a smoker or heavy drinker, quitting these habits can greatly improve your overall cardiovascular health. Seek support from healthcare professionals or programs specifically designed to help individuals quit smoking or reduce their alcohol consumption.
Get Regular Health Check-ups:

Regular health check-ups are an essential part of maintaining overall well-being and reducing the risk of cardiac arrest. These check-ups provide valuable insights into your current health status, allowing healthcare professionals to detect any potential issues or abnormalities before they become serious concerns.
During a routine check-up, your doctor will assess various aspects of your health, including blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and body mass index (BMI). High blood pressure and high cholesterol are major risk factors for heart disease and can significantly increase the likelihood of experiencing a cardiac event.
Furthermore, regular screenings may include tests to evaluate specific aspects of cardiovascular function, like electrocardiograms (ECG’s) or stress tests. These diagnostic tools allow medical professionals to identify underlying conditions that could potentially lead to cardiac complications if left untreated.
By scheduling regular check-ups with your healthcare provider, you demonstrate a proactive approach toward preventing heart problems. Remember that prevention is always better than cure when it comes to matters of the heart. So don’t neglect these crucial appointments – they could make all the difference in safeguarding against cardiac arrest.
Learn CPR and How to Use an AED:
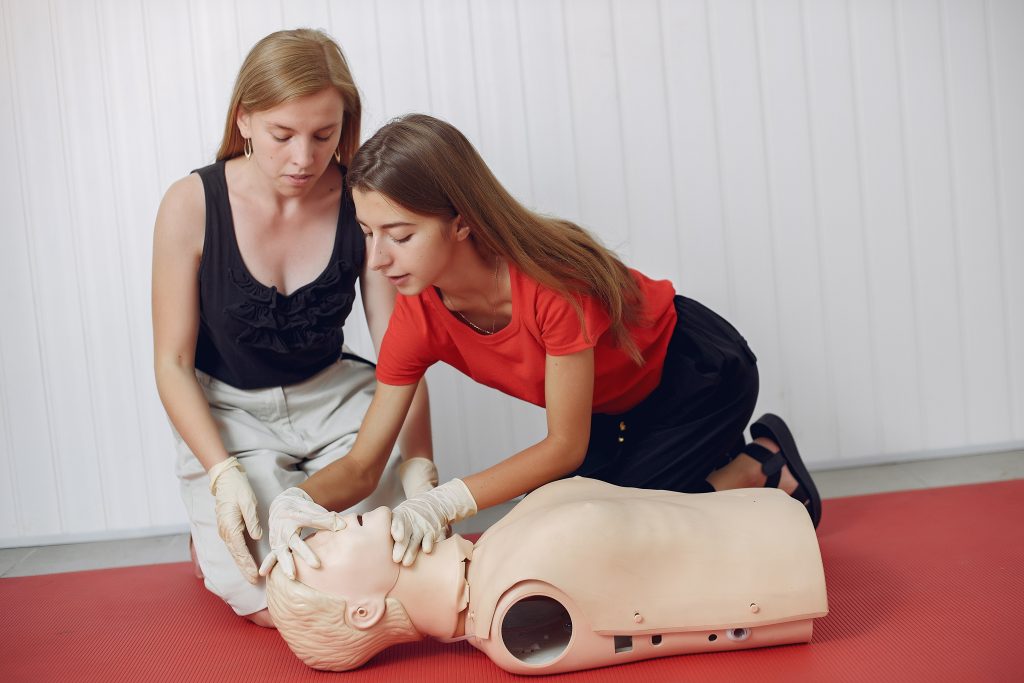
Cardiac arrest can strike anyone, anywhere, at any time. It is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate attention. That’s why learning cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and how to use an automated external defibrillator (AED) is crucial.
CPR is a technique used to keep blood flowing through the body when someone’s heart has stopped beating. It involves compressions on the chest to mimic the pumping action of the heart. Learning CPR can mean the difference between life and death for someone experiencing cardiac arrest.
An AED is a portable device that delivers an electric shock to restore normal heart rhythm in cases of sudden cardiac arrest. These devices are designed for use by nonmedical personnel in emergencies and are becoming more common in public places like airports, shopping malls, and schools.
Learning CPR and how to use an AED doesn’t require extensive medical training. Many organizations offer courses that teach these life-saving skills in just a few hours. By taking a course, you will gain confidence in your ability to respond effectively during emergencies.
Imagine being able to save a loved one or even a stranger’s life because you knew what steps to take during those critical moments before professional help arrives. The knowledge gained from learning CPR and how to use an AED empowers individuals with the skills needed to make a real difference when it matters most.
By following these simple yet effective steps consistently, you are taking control of your cardiovascular health while reducing the risk of cardiac arrest. Remember that every positive change counts towards building a healthier future for yourself!
So what are you waiting for? Start implementing these strategies today! Your heart will thank you later.